















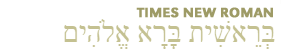
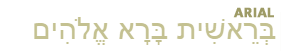

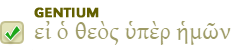
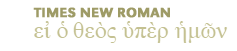
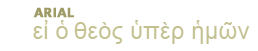

The author or authors of 1 and 2 Samuel are not known. These books recount the stories of Samuel, Saul, and David. Saul's reign began between 1050-1030 b.c. and ended in 1010. David then reigned until 971. The books were probably written soon after the end of his reign.
The central theme of the books of Samuel is how the Lord (1) established a dynasty ("house") in Israel for David rather than Saul and (2) how he chose Jerusalem as the place where David's successor would establish the temple ("house") for the worship of the divine King Yahweh.
The purpose of 1 Samuel is to highlight two major events: the establishment of the monarchy in Israel (chs. 8-12); and the rise of David to be king after Saul (chs. 16-31). After ruling for a while, Saul was rejected by the Lord in favor of David (chs. 15-16), though Saul stayed on the throne until his death at Mount Gilboa (ch. 31). Later, in 2 Samuel 7, God promises David and his house an eternal dynasty. The book of 1 Samuel establishes the principle that obedience to the word of God is the necessary condition for a king to be acceptable to the God of Israel.
First and Second Samuel deal with a transitional period in the history of ancient Israel. There is a transition of leadership first from the priest Eli to the judge Samuel, then from the judge Samuel to the king Saul, and then from Saul to David. Samuel thus is the link between the judgeship and the kingship in Israel. He is the prophet God uses to anoint both Saul and David. The kingdom of Saul was also transitional. Under Saul, Israel was more than a loose confederation that gathered together whenever there was a common threat, but there was no strong central rule such as existed later. The story of the rise of David in the second half of 1 Samuel prepares for the full-scale kingship of David in 2 Samuel.
The themes of 1 Samuel are related to the themes of 2 Samuel: the sovereign God, who has guided David's life, chooses David as the ruler of God's people. God pledges to David an eternal covenant. David thus becomes the prototype of the future Messiah, Jesus Christ.
The book of 1 Samuel is set in Israel during the transition between the period of the judges and the period of the monarchy. It opens with Samuel's birth and then describes his role as judge over Israel. When the people ask for a king, the Lord instructs Samuel to anoint Saul as Israel's first king.
The book of 2 Samuel recounts David's reign over Israel and his battles to establish Israel as the dominant power in Syria and Palestine. David expanded Israel's borders from Saul's smaller territory. By the end of his reign, David controlled all of Israel, Edom, Moab, Ammon, Syria, and Zobah. Other kingdoms, such as Tyre and Hamath, established treaties with him.

The ESV Global Study Bible
Copyright © 2012 by Crossway.
All rights reserved.
Used by permission.
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
