
















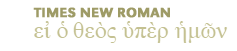
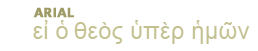

References for 2Sa 3:13 — 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
The text nowhere directly identifies its author, but traditionally he has been called "the Chronicler." He was either a priest or Levite who was employed in the service of the temple during the Persian period (539-332 b.c.). He had scribal training and access to the temple records.
The central theme of Chronicles is God's covenant with David as the basis of Israel's life and hope. The Davidic covenant is expressed in two institutions: the monarchy and the temple. These institutions are related (1 Chron. 17:10b-14), and together they represent God's kingdom in Israel (2 Chron. 13:5, 8). The Davidic covenant does not replace the Mosaic covenant but builds on it for the new age of the monarchy and the temple.
Judah and Benjamin, the only surviving tribes of Israel, had returned to the land after the Babylonian exile. They had rebuilt the temple in Jerusalem. But in many ways it seemed like they were still in exile (see Ezra 9:6-15; Neh. 9:32-36). There were questions about Israel's place in God's purposes and the meaning of his ancient promises to David. With such questions in mind, the Chronicler wrote his books to promote spiritual and social renewal. He presented an interpretation of Israel's past, drawing mainly on the books of Samuel and Kings. He showed how the nation's unfaithfulness to God had led to disaster but also how its faithful kings and people had experienced God's blessing.
David's many battles eventually established Israel as the dominant power in Syria and Palestine. David expanded Israel's borders until, by the end of his reign, he controlled all of Israel, Edom, Moab, Ammon, Syria, and Zobah. Other kingdoms, such as Tyre and Hamath, made treaties with him.
Solomon's reign marked the high point of Israel's power and wealth in biblical times. His father David had given him a kingdom that included Edom, Moab, Ammon, Syria, and Zobah. Solomon would later bring the kingdom of Hamath-zobah under his dominion as well, and his marriage to Pharaoh's daughter sealed an alliance with Egypt. His expansive kingdom controlled important trade routes between several major world powers, including Egypt, Arabia, Mesopotamia, and Anatolia (Asia Minor).

The ESV Global Study Bible
Copyright © 2012 by Crossway.
All rights reserved.
Used by permission.
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
