
















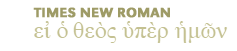
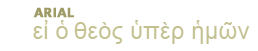

Click here to view listing below for Act 15:5
'And certain men which came down from Judaea taught the brethren, and said, Except ye be circumcised after the manner of Moses, ye cannot be saved. 2. When therefore Paul and Barnabas had no small dissension and disputation with them, they determined that Paul and Barnabas, and certain other of them, should go up to Jerusalem unto the apostles and elders about this question. 3. And being brought on their way by the church, they passed through Phenice and Samaria, declaring the conversion of the Gentiles: and they caused great joy unto all the brethren. 4. And when they were come to Jerusalem, they were received of the church, and of the apostles and elders, and they declared all things that God had done with them. 5. But there rose up certain of the sect of the Pharisees which believed, saying, That it was needful to circumcise them, and to command them to keep the law of Moses. 6. And the apostles and elders came together 'for to consider of this matter.'—Acts 15:1-6.
The question as to the conditions on which Gentiles could be received into Christian communion had already been raised by the case of Cornelius, but it became more acute after Paul's missionary journey. The struggle between the narrower and broader views was bound to come to a head. Traces of the cleft between Palestinian and Hellenist believers had appeared as far back as the 'murmuring' about the unfair neglect of the Hellenist widows in the distribution of relief, and the whole drift of things since had been to widen the gap.
Whether the 'certain men' had a mission to the Church in Antioch or not, they had no mandate to lay down the law as they did. Luke delicately suggests this by saying that they 'came down from Judaea,' rather than from Jerusalem. We should be fair to these men, and remember how much they had to say in defence of their position. They did not question that Gentiles could be received into the Church, but 'kept on teaching' (as the word in the Greek implies) that the divinely appointed ordinance of circumcision was the 'door' of entrance. God had prescribed it, and through all the centuries since Moses, all who came into the fold of Israel had gone in by that gate. Where was the commandment to set it aside? Was not Paul teaching men to climb up some other way, and so blasphemously abrogating a divine law?
No wonder that honest believers in Jesus as Messiah shrank with horror from such a revolutionary procedure. The fact that they were Palestinian Jews, who had never had their exclusiveness rubbed off, as Hellenists like Paul and Barnabas had had, explains, and to some extent excuses, their position. And yet their contention struck a fatal blow at the faith, little as they meant it. Paul saw what they did not see—that if anything else than faith was brought in as necessary to knit men to Christ, and make them partakers of salvation, faith was deposed from its place, and Christianity sank back to be a religion of 'works.' Experience has proved that anything whatever introduced as associated with faith ejects faith from its place, and comes to be recognised as the means of salvation. It must be faith or circumcision, it cannot be faith and circumcision. The lesson is needed to-day as much as in Antioch. The controversy started then is a perennial one, and the Church of the present needs Paul's exhortation, 'Stand fast therefore in the liberty wherewith Christ hath made us free, and be not entangled again with the yoke of bondage.'
The obvious course of appealing to Jerusalem was taken, and it is noteworthy that in verse 2 the verb 'appointed' has no specified subject. Plainly, however, it was the Church which acted, and so natural did that seem to Luke that he felt it unnecessary to say so. No doubt Paul concurred, but the suggestion is not said to have come from him. He and Barnabas might have asserted their authority, and declined to submit what they had done by the Spirit's guidance to the decision of the Apostles, but they seek the things that make for peace.
No doubt the other side was represented in the deputation. Jerusalem was the centre of unity, and remained so till its fall. The Apostles and elders were the recognised leaders of the Church. Elders here appear as holding a position of authority; the only previous mention of them is in Acts 11:30, where they receive the alms sent from Antioch. It is significant that we do not hear of their first appointment. The organisation of the Church took shape as exigencies prescribed.
The deputation left Antioch, escorted lovingly for a little way by the Church, and, journeying by land, gladdened the groups of believers in 'Phenicia and Samaria' with the news that the Gentiles were turning to God. We note that they are not said to have spoken of the thorny question in these countries, and that it is not said that there was joy in Judaea. Perhaps the Christians in it were in sympathy with the narrower view.
The first step taken in Jerusalem was to call a meeting of the Church to welcome the deputation. It is significant that the latter did not broach the question in debate, but told the story of the success of their mission. That was the best argument for receiving Gentile converts without circumcision. God had received them; should not the Church do so? Facts are stronger than theories. It was Peter's argument in the case of Cornelius: they 'have received the Holy Ghost as well as we,' 'who was I, that I could withstand God?' It is the argument which shatters all analogous narrowing of the conditions of Christian life. If men say, 'Except ye be' this or that 'ye cannot be saved,' it is enough to point to the fruits of Christian character, and say, 'These show that the souls which bring them forth are saved, and you must widen your conceptions of the possibilities to include these actualities.' It is vain to say 'Ye cannot be' when manifestly they are.
But the logic of facts does not convince obstinate theorists, and so the Judaising party persisted in their 'It is needful to circumcise them.' None are so blind as those to whom religion is mainly a matter of ritual. You may display the fairest graces of Christian character before them, and you get no answer but the reiteration of 'It is needful to circumcise you.' But on their own ground, in Jerusalem, the spokesmen of that party enlarged their demands. In Antioch they had insisted on circumcision, in Jerusalem they added the demand for entire conformity to the Mosaic law. They were quite logical; their principle demanded that extension of the requirement, and was thereby condemned as utterly unworkable. Now that the whole battery was unmasked the issue was clear—Is Christianity to be a Jewish sect or the universal religion? Clear as it was, few in that assembly saw it. But the parting of the ways had been reached.
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
