
















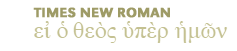
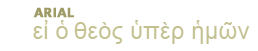

Click here to view listing below for Mat 3:2
1. (2 Corinthians 7:1a) In light of God’s promises.
Therefore, having these promises.
a. Therefore, having these promises: This is Paul’s natural conclusion to 2 Corinthians 6:14-18. In that passage, Paul wrote about the need to separate from worldly influences so that we can live a close life with God.
b. These promises: The commandment to come out from among them and be separate (2 Corinthians 6:17) is coupled with a promise: I will receive you. I will be a Father to you, and you shall be My sons and daughters (2 Corinthians 6:18). If we separate ourselves from worldly thinking and acting, we are promised a closer relationship with God.
2. (2 Corinthians 7:1b) Two things to do in light of God’s promises.
Beloved, let us cleanse ourselves from all filthiness of the flesh and spirit, perfecting holiness in the fear of God.
a. Cleanse ourselves from all filthiness: This is what we take away. There is a cleansing that God alone does in our lives, but there is also a cleansing that God wants to do in cooperation with us. Here, Paul writes about a cleansing that isn’t just something God does for us as we sit passively; this is a self-cleansing for intimacy with God that goes beyond a general cleansing for sin.
i. There is a main aspect of cleansing that comes to us as we trust in Jesus and His work on our behalf. This work of cleansing is really God’s work in us and not our work. This is the sense of 1 John 1:9: If we confess our sins, He is faithful and just to forgive us our sins and to cleanse us from all unrighteousness.
ii. But there is another aspect of cleansing that God looks for us to do with the participation of our own will and effort; not that it is our work apart from God, but it is a work that awaits our will and effort: let us cleanse ourselves. This aspect of cleansing is mostly connected with intimacy with God and usefulness for service.
iii. “How can those expect God to purify their hearts who are continually indulging their eyes, ears, and hands in what is forbidden, and in what tends to increase and bring into action all the evil propensities of the soul?” (Clarke)
b. From all filthiness of the flesh and spirit: We often think of purity before the Lord only in terms of cleansing from all filthiness of the flesh, but there is also a filthiness of the… spirit to cleanse ourselves from.
i. Sometimes it is easier to deal with the filthiness of the flesh than the filthiness… of the spirit. During Jesus’ earthly ministry, those who were stained by the filthiness of the flesh (such as harlots and tax collectors) found it easy to come to Jesus. But those stained by the filthiness… of the spirit (such as the scribes and Pharisees) found it very hard to come to Jesus.
ii. Our pride, our legalism, our self-focus, our self-righteousness, our bitterness, and our hatred can all be far worse to deal with than the more obvious sins of the flesh. “There is a defilement of the spirit which is independent of the defilement of the flesh. The spirit can be defiled in many ways. I sometimes think that the sins of the spirit are more deadly than the sins of the flesh.” (Morgan)
iii. “I wish we were more concerned about cleansing ourselves from the filthiness of the spirit. I am inclined to think that some men heedlessly pollute their spirits; I mean that they do it willfully.” (Spurgeon)
c. Perfecting holiness in the fear of God: This is something to add. Paul isn’t writing about some state of sinless perfection. Perfecting has the idea of “complete” and “whole.” Instead of a state of sinless perfection, Paul writes about a complete, “whole,” holiness.
i. It isn’t enough to only cleanse ourselves from all filthiness. The Christian life is not only getting rid of evil but continually doing and becoming good.
d. Cleanse ourselves: Note that Paul includes himself among the Corinthian Christians in the category of those who need to be cleansed. If Paul includes himself among those who needed to be cleansed, then what about us?
i. “I suppose that, the nearer we get to heaven, the more conscious we shall be of our imperfections. The more light we get, the more we discover our own darkness. That which is scarcely accounted sin by some men, will be a grievous defilement to a tender conscience. It is not that we are greater sinners as we grow older, but that we have a finer sensibility of sin, and see that to be sin which we winked at in the days of our ignorance.” (Spurgeon)
ii. “I remember hearing a man say that he had lived for six years without having sinned in either thought, or word, or deed. I apprehended that he committed a sin then, if he had never done so before, in uttering such a proud, boastful speech.” (Spurgeon)
iii. But we must take care that we cleanse ourselves and not concern ourselves with cleansing others. Most of the time we are more concerned with the holiness of others than our own holiness! “It were more in accordance with our tastes to cleanse other people, and attempt a moral reformation among our neighbors. Oh! it is easy to find out other men’s faults, and to bring the whole force of our mind to inveigh against them.” (Spurgeon)
1. (2 Corinthians 7:2-3) Paul’s appeal: Open your hearts to us.
Open your hearts to us. We have wronged no one, we have corrupted no one, we have cheated no one. I do not say this to condemn; for I have said before that you are in our hearts, to die together and to live together.
a. Open your hearts: In 2 Corinthians 6:11-13, Paul wrote: We have spoken openly to you, our heart is wide open… you also be open. Then, in 2 Corinthians 6:14-7:1, he dealt with the worldliness that kept the Corinthians from having the kind of open relationship they should have with Paul. Now, in writing open your hearts to us, Paul returns to idea he left off with in 2 Corinthians 6:11-13.
i. Paul was completely honest with the Corinthian Christians. Now he tells them they must be honest also and be open to seeing the truth about Paul and his ministry.
ii. The Corinthian Christians believed many bad things about Paul — that God wasn’t using him, that he didn’t have the kind of image, authority, or power an apostle should have — but their problem was not an information problem. Their problem was with their hearts. Their hearts had been open to the world but not to Paul. In the “unequally yoked” passage, Paul told them to close their hearts to the world. Now it is time to open their hearts to him.
b. We have wronged no one, we have corrupted no one, we have defrauded no one. Paul reminds the Corinthians of what they already know: Despite what some troublemakers said about Paul, they had no good reason to criticize him.
i. When Paul claims he defrauded no one, remember that he was organizing a collection for poor Christians in Judea and had responsibility over a significant amount of money (1 Corinthians 16:1-4).
c. I do not say this to condemn: Paul’s desire isn’t to condemn the Corinthian Christians but to restore the bonds of fellowship he once had with them. Paul really loved the Corinthian Christians: I have said before that you are in our hearts, to die together and to live together.
i. Paul confronted the Corinthian Christians, but he did not want to condemn them. It is possible to confront without condemning, though those who are being confronted rarely think so.
2. (2 Corinthians 7:4-7) Paul is encouraged by good news from the Corinthian Christians.
Great is my boldness of speech toward you, great is my boasting on your behalf. I am filled with comfort. I am exceedingly joyful in all our tribulation. For indeed, when we came to Macedonia, our bodies had no rest, but we were troubled on every side. Outside were conflicts, inside were fears. Nevertheless God, who comforts the downcast, comforted us by the coming of Titus, and not only by his coming, but also by the consolation with which he was comforted in you, when he told us of your earnest desire, your mourning, your zeal for me, so that I rejoiced even more.
a. Great is my boldness of speech toward you, great is my boasting on your behalf: Yes, Paul has been bold in his criticism to the Corinthians, but he was also bold in his boasting about them.
b. I am filled with comfort. I am exceedingly joyful in all our tribulation… when he told us of your earnest desire, your zeal for me, so that I rejoiced even more: Despite the many trials Paul faced (from both within and without), he found joy, and part of that joy was good news from the Corinthian Christians.
i. I am exceedingly joyful in all our tribulation: This phrase exceedingly joyful could be expressed as “I super-abound in joy; I have a joy beyond expression.” Some think that God wants us to endure tribulation with a blank, stoic face — the “stiff upper lip” — but God wants more from us than that. He wants us to super-abound in joy even in all our tribulation.
ii. God brought comfort to Paul by hearing about the work God did among the Corinthian Christians. “No circumstances of personal affliction can dim the gladness of seeing souls grow in the grace of the Lord Jesus.” (Morgan)
iii. When Paul speaks of the coming of Titus, he actually picks up where he left off in 2 Corinthians 2:13. In a sense, 2 Corinthians 2:14 to 7:4 is one long digression — led by God of course and containing some of the richest treasure of the New Testament.
c. Our flesh had no rest, but we were troubled on every side: Paul had a hard time in Macedonia, but Titus came to Paul when he was in Macedonia and he brought a good report of how the Corinthian Christians were turning back to Jesus and to Paul.
i. In spite of all his frustrations with the Corinthians and in the midst of all his afflictions in ministry, Paul had real confidence and hope because Titus brought him a good report of how things were going in Corinth.
ii. In 2 Corinthians 1:3, Paul declared that God is the God of all comfort. Here, Paul experienced that comfort through the coming of Titus and the news from Corinth. Paul experienced the comfort of God through human instruments. Often when we turn away from people, we turn away from the comfort God wants to give us.
d. Outside were conflicts, inside were fears: This was Paul’s life in ministry. It was a life of great blessing but also a life of many conflicts and fears. On the outside, Paul was constantly in conflict with enemies of the gospel and worldly minded Christians. On the inside, Paul daily battled with the stress and anxiety of ministry.
e. Your earnest desire, your mourning, your zeal for me: Titus told Paul that the Corinthian Christians had not forsaken him completely. In fact, these things (desire… mourning… zeal) proved God really was doing a work in the Corinthian Christians, and knowing that was a comfort to Paul.
3. (2 Corinthians 7:8-12) The severe letter and its effect.
For even if I made you sorry with my letter, I do not regret it; though I did regret it. For I perceive that the same epistle made you sorry, though only for a while. Now I rejoice, not that you were made sorry, but that your sorrow led to repentance. For you were made sorry in a godly manner, that you might suffer loss from us in nothing. For godly sorrow produces repentance leading to salvation, not to be regretted; but the sorrow of the world produces death. For observe this very thing, that you sorrowed in a godly manner: What diligence it produced in you, what clearing of yourselves, what indignation, what fear, what vehement desire, what zeal, what vindication! In all things you proved yourselves to be clear in this matter. Therefore, although I wrote to you, I did not do it for the sake of him who had done the wrong, nor for the sake of him who suffered wrong, but that our care for you in the sight of God might appear to you.
a. For even if I made you sorry with my letter: What letter? This probably is not the letter of 1 Corinthians but a letter that Paul wrote in between 1 and 2 Corinthians.
i. It helps if we remember the sequence of events. Things were going badly among the Christians in Corinth, and in an attempt to get them on track, Paul made a quick, unplanned visit that only seemed to make things worse (the “sorrowful visit” mentioned in 2 Corinthians 2:1). After the failure of this visit, Paul decided not to visit Corinth again in person at the time but instead sent Titus to them with a strong letter of rebuke. Paul was very worried about how the Corinthians would receive the letter and whether it would turn them to Jesus or just make them angry. When Titus came back with good news from the Corinthian Christians, Paul was greatly relieved.
b. I do not regret it; though I did regret it: When Paul first wrote the “sorrowful letter” carried by Titus, he didn’t enjoy the idea of being so confrontational with the Corinthian Christians, even though they deserved it. That’s why he wrote, “though I did regret it.” At the same time, when Titus came back and reported the response of the Corinthian Christians (the earnest desire… mourning and zeal mentioned in 2 Corinthians 7:7), Paul was happy for the effect the letter had. That’s why he wrote, “I do not regret it.”
c. The same epistle made you sorry, though only for a while: “In sin, the pleasure passeth, the sorrow remaineth; but in repentance, the sorrow passeth, the pleasure abideth for ever. God soon poureth the oil of gladness into broken hearts.” (Trapp)
d. Not that you were made sorry, but that your sorrow led to repentance. Paul makes a clear separation between sorrow and repentance. They are not the same things! One can be sorry for their sin without repenting from their sin. Sorrow describes a feeling, but repentance describes a change in both the mind and in the life.
i. “Repentance is not sorrow only. It may be unaccompanied by sorrow… at the time, but sorrow will always follow, sorrow for the past; but this change of mind is the great thing.” (Morgan)
ii. “Sorrow alone accomplishes nothing. Peter was sorry he denied Christ, and he repented. Judas was sorry he betrayed Christ but, instead of repenting, he killed himself.” (Smith)
iii. “Repentance” sounds like a harsh word to many but it is an essential aspect of the gospel and has been called “the first word of the gospel.” When John the Baptist preached, he said Repent, for the kingdom of heaven is at hand! (Matthew 3:2). When Jesus began to preach, He said Repent, for the kingdom of heaven is at hand (Matthew 4:17). When Peter preached on the day of Pentecost, he told his listeners to repent (Acts 2:38).
iv. What was it that the Corinthian Christians had to repent of? Take your pick! It could have been any number of things, but no doubt it also included this: There were probably some “anti-Paul” people who criticized the absent apostle severely and unfairly, and the Corinthians did not defend their godly spiritual father before these detractors.
e. You were made sorry in a godly manner: Paul made the Corinthian Christians feel bad for their sin, but he did it in a godly way. He used the truth, not lies or exaggeration. He was honest, not using hidden agendas and manipulation. He simply told the truth in love. Not every preacher or every person can say they do the same as Paul did and it isn’t right to try to make someone sorry in an ungodly manner.
i. That you might suffer loss from us in nothing shows why it is important to only make others sorrow in a godly manner. You may succeed in making them feel bad (sorrow), but the relationship you have with that person will suffer loss. You can win the “battle” yet lose the “war.” Paul wanted to protect his relationship with the Corinthian Christians, so he would only make them sorry in a godly manner.
f. Godly sorrow produces repentance unto salvation: Does this mean we are saved by our repentance? Not exactly. Repentance “is not the ground of our salvation; but it is a part of it and necessary condition of it. Those who repent are saved; the impenitent perish. Repentance is therefore unto salvation.” (Hodge)
i. Repentance must never be thought of as something we must do before we can come back to God. Repentance describes the very act of coming to God. You can’t turn towards God without turning from the things He is against. “People seem to jump into faith very quickly nowadays. I do not disapprove of that happy leap; but still, I hope my old friend repentance is not dead. I am desperately in love with repentance; it seems to me to be the twin-sister to faith.” (Spurgeon)
ii. Sorrow in itself doesn’t produce anything except bad feelings, but godly sorrow produces repentance. Since repentance is a change (in both thinking and action), we can tell if sorrow is really godly by seeing if it produces repentance. So godly sorrow cannot be measured by feelings or tears, only by what it produces.
iii. “How sorry do you think you have to be? What is the purpose of your sorrow for sin? It is to bring you to trust in the atoning work of our Lord Jesus Christ. It is not your sorrow that cleanses you from sin, but His blood. It is the goodness of God that leads a man to repentance. Has your sorrow for sin led you at one time or another fling all the burden of it at the feet of a crucified, risen Saviour? If it hasn’t, anything short of that is what Paul here calls sorrow that leads to death.” (Redpath)
iv. Real repentance acts. “If thou repent with a contradiction (saith Tertullian) God will pardon thee with a contradiction. Thou repentest, and yet continuest in thy sin. God will pardon thee, and yet send thee to hell. There is pardon with a contradiction.” (John Trapp wrote these hard and striking words)
g. Not to be regretted: This is because godly sorrow does such a great work. It doesn’t feel good, but it does a good work. The sorrow of the world is different, because it produces death.
i. When sorrow is received or borne in a worldly way, it has the deadly effect of producing resentment or bitterness. We can regret that kind of sorrow. Godly sorrow produces repentance unto salvation that is not to be regretted. “A repentance as a man shall never have cause to repent of. Job cursed the day of his birth; but no man was ever heard to curse the day of his new birth.” (Trapp)
ii. “In repentance there is a bitter sweetness, or a sweet bitterness — which shall I call it? — of which, the more you have, the better it is for you. I can truly say that I hardly know a diviner joy than to lay my head in my Heavenly Father’s bosom and to say, ‘Father, I have sinned, but thou hast forgiven me; and, oh, I do love thee!’” (Spurgeon)
h. What diligence it produced in you, what clearing of yourselves, what indignation, what fear, what vehement desire, what zeal, what vindication! All of these things showed that the sorrow of the Corinthian Christians worked real repentance.
i. What diligence: Godly sorrow produces, and repentance shows diligence. Repentance means to turn around, and it takes diligence to stay turned around. If one gives up easily, they can never walk in repentance, though they may perform acts of repentance.
ii. What clearing of yourselves: Godly sorrow produces, and repentance shows a clearing. It is a clearing of guilt and shame, from knowing that we brought our sin to God and we now walk in the right way.
iii. What indignation: Godly sorrow produces, and repentance shows indignation. We are indignant at our selves for our foolishness in sin. This is the kind of attitude that makes repentance last. “I am glad that the Bible allows me to get mad, mad with the devil! To think that he had the audacity to pull me down and make me do that! What indignation, what fury at sin and all the agencies of Satan!” (Redpath)
iv. What fear: Godly sorrow produces, and repentance shows a fear that we would ever fall into the same sin again. Paul isn’t writing about a fear of God here as much as a fear of sin, and fear of our own weakness toward sin.
v. What vehement desire: Godly sorrow produces, and repentance shows vehement desire. This is a heart that really desires purity and godliness and does not want to sin any more. This vehement desire is expressed through heartfelt prayer and total dependence on God.
vi. What zeal: Godly sorrow produces, and repentance shows zeal. The ancient Greek word speaks of heat; we are hot towards God and His righteousness, and hot against sin and impurity. Instead of laziness, we have zeal in our walk with the Lord.
vii. What vindication: Godly sorrow produces, and repentance shows vindication. You are vindicated as a Christian, even though you have sinned. No one can doubt it because the measure of a Christian is not whether or not they sin, but whether or not they repent.
viii. Proved yourself to be clear: When repentance is marked by the preceding characteristics, we are clear of guilt and sin. The stain of sin is gone! We can feel it, and others can see it. “Happy is that man who has had enough of the smart of sin to make it sour and bitter to him all the rest of his days; so that now, with changed heart, and renewed spirit, he perseveres in the ways of God, never thinking of going back, but resolved ‘through floods or flames’ to force his way to heaven, to be, by divine grace, master over every sin that assails him.” (Spurgeon)
i. In all things you proved yourselves to be clear: Their actions of repentance proved them to be clear. It wasn’t words or feelings that proved them to be clear, but actions.
i. “Godly sorrow that leads to repentance, therefore, is a sorrow that leads to a change of purpose, of intention, and of action. It is not the sorrow of idle tears; it is not crying by your bedside because once again you have failed; nor is it vain regret, wishing things had never happened, wishing you could live the moments again. No, it is not that. It is a change of purpose and intentions, a change of direction and action.” (Redpath)
j. In this matter: Paul is using godly discretion by not bringing up the whole affair again from the beginning. There was someone who had done wrong (him who had done the wrong) and there was someone who had been wronged (him who suffered wrong). But there was no need to go through the whole mess again.
k. I did not do it for the sake: Paul’s purpose in writing the “sorrowful letter” was not to take sides in a dispute among the Corinthian Christians. His purpose was to demonstrate his concern (that our care for you in the sight of God might appear to you).
i. Paul’s concern for the Corinthian Christians was evident but amazing. “From all appearance there was never a Church less worthy of an apostle’s affections than this Church was at this time; and yet no one ever more beloved.” (Clarke)
4. (2 Corinthians 7:13-16) How Titus regarded the Corinthian Christians after his visit.
Therefore we have been comforted in your comfort. And we rejoiced exceedingly more for the joy of Titus, because his spirit has been refreshed by you all. For if in anything I have boasted to him about you, I am not ashamed. But as we spoke all things to you in truth, even so our boasting to Titus was found true. And his affections are greater for you as he remembers the obedience of you all, how with fear and trembling you received him. Therefore I rejoice that I have confidence in you in everything.
a. His spirit has been refreshed by you all: The experience of Titus in Corinth and his report from there were sure evidence that the Corinthian Christians had a change of mind.
b. If in anything I have boasted to him about you: Paul had “hopefully” boasted to Titus that the Corinthian Christians would respond well to the severe letter. Probably Titus was not so sure! But Paul’s boasting to Titus was found true.
c. His affections are great for you: Paul assures the Corinthian Christians that Titus loves them more than ever now. Probably Titus saw a lot of ugliness among the Corinthian Christians, and from this he may have had a “chip on his shoulder” against them. So Paul wants them to know that after he saw and reported their repentance, Titus loved them more than ever.
d. I rejoice that I have confidence in you in everything: Is Paul being sarcastic here? Probably not. He is probably simply trying to encourage the Corinthians, showing them that he is convinced their repentance was genuine.
i. “Thus by praising them, he further winneth upon them, whom before he had more sharply handled. Sour and sweet make the best sauce.” (Trapp)
ii. At the end of this chapter, Paul praises the Corinthian Christians and they seem to be in a place of victory. But in the “sorrowful letter” (mentioned in 2 Corinthians 2:1) there was no praise. What was the difference? Their real repentance, reported by Titus and commented on by Paul in this chapter.
iii. All through this chapter we see how concerned Paul was about his relationship with the Corinthian Christians. This shows that people were just as important to Paul as ministry. He didn’t want to do “ministry” at the expense of his relationships with people.
©2018 David Guzik – No distribution beyond personal use without permission
References:
Updated: August 2022
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
