











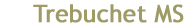




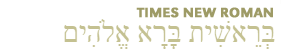
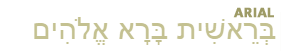

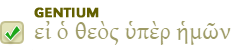
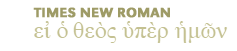
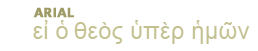

Click here to view listing below for Act 13:15
When the various NT books were formally brought together into one collection shortly after A.D. 100, the titles were added for convenience. This epistle’s title bears the traditional Greek title, “To the Hebrews,” which was attested by at least the second century A.D. Within the epistle itself, however, there is no identification of the recipients as either Hebrews (Jews) or Gentiles. Since the epistle is filled with references to Hebrew history and religion and does not address any particular Gentile or pagan practice, the traditional title has been maintained.
The author of Hebrews is unknown. Paul, Barnabas, Silas, Apollos, Luke, Philip, Priscilla, Aquila, and Clement of Rome have been suggested by different scholars, but the epistle’s vocabulary, style, and various literary characteristics do not clearly support any particular claim. It is significant that the writer includes himself among those people who had received confirmation of Christ’s message from others (2:3). That would seem to rule out someone like Paul who claimed that he had received such confirmation directly from God and not from men (Gal. 1:12). Whoever the author was, he preferred citing OT references from the Greek OT (LXX) rather than from the Hebrew text. Even the early church expressed various opinions on authorship, and current scholarship admits the puzzle still has no solution. Therefore, it seems best to accept the epistle’s anonymity. Ultimately, of course, the author was the Holy Spirit (2 Pet. 1:21).
The use of the present tense in 5:1–4; 7:21, 23, 27, 28; 8:3–5, 13; 9:6–9, 13, 25; 10:1, 3, 4, 8, 11; and 13:10, 11 would suggest that the Levitical priesthood and sacrificial system were still in operation when the epistle was composed. Since the temple was destroyed by General (later Emperor) Titus Vespasian in A.D. 70, the epistle must have been written prior to that date. In addition, it may be noted that Timothy had just been released from prison (13:23) and that persecution was becoming severe (10:32–39; 12:4; 13:3). These details suggest a date for the epistle around A.D. 67–69.
Emphases on the Levitical priesthood and on sacrifices, as well as the absence of any reference to the Gentiles, support the conclusion that a community of Hebrews was the recipient of the epistle. Although these Hebrews were primarily converts to Christ, there were probably a number of unbelievers in their midst, who were attracted by the message of salvation, but who had not yet made a full commitment of faith in Christ (see Interpretive Challenges). One thing is clear from the contents of the epistle: the community of Hebrews was facing the possibility of intensified persecution (10:32–39; 12:4). As they confronted this possibility, the Hebrews were tempted to cast aside any identification with Christ. They may have considered demoting Christ from God’s Son to a mere angel. Such a precedent had already been set in the Qumran community of messianic Jews living near the Dead Sea. They had dropped out of society, established a religious commune, and included the worship of angels in their brand of reformed Judaism. The Qumran community had even gone so far as to claim that the angel Michael was higher in status than the coming Messiah. These kinds of doctrinal aberrations could explain the emphasis in Hebrews chapter one on the superiority of Christ over the angels.
Possible locations for the recipients of the epistle include Palestine, Egypt, Italy, Asia Minor, and Greece. The community that was the primary recipient may have circulated the epistle among those of Hebrew background in neighboring areas and churches. Those believers probably had not seen Christ personally. Apparently, they had been evangelized by “those who heard” Christ and whose ministries had been authenticated “with signs and wonders, with various miracles” (2:3, 4). Thus the recipients could have been in a church outside Judea and Galilee or in a church in those areas, but established among people in the generation following those who had been eyewitnesses of Christ. The congregation was not new or untaught (“by this time you ought to be teachers”) yet some of them still needed “milk and not solid food” (5:12).
“Those from Italy” (13:24) is an ambiguous reference since it could mean either those who had left Italy and were living elsewhere, or those who were still in Italy and being singled out as native residents of that country. Greece or Asia Minor must also be considered because of the apparently early establishment of the church there, and because of the consistent use of the LXX.
The generation of Hebrews receiving this epistle had practiced the Levitical sacrifices at the temple in Jerusalem. Jews living in exile had substituted the synagogue for the temple but still felt a deep attraction to the temple worship. Some had the means to make regular pilgrimages to the temple in Jerusalem. The writer of this epistle emphasized the superiority of Christianity over Judaism and the superiority of Christ’s once-for-all sacrifice over the repeated and imperfect Levitical sacrifices observed in the temple.
Since the book of Hebrews is grounded in the work of the Levitical priesthood, an understanding of the book of Leviticus is essential for properly interpreting Hebrews. Israel’s sin had continually interrupted God’s fellowship with His chosen and covenant people, Israel. Therefore, He graciously and sovereignly established a system of sacrifices that symbolically represented the inner repentance of sinners and His divine forgiveness. However, the need for sacrifices never ended because the people and priests continued to sin. The need of all mankind was for a perfect priest and a perfect sacrifice that would once and for all actually remove sin. God’s provision for that perfect priest and sacrifice in Christ is the central message of Hebrews.
The epistle to the Hebrews is a study in contrast, between the imperfect and incomplete provisions of the Old Covenant, given under Moses, and the infinitely better provisions of the New Covenant offered by the perfect High-Priest, God’s only Son and the Messiah, Jesus Christ. Included in the “better” provisions are: a better hope, testament, promise, sacrifice, substance, country, and resurrection. Those who belong to the New Covenant dwell in a completely new and heavenly atmosphere, they worship a heavenly Savior, have a heavenly calling, receive a heavenly gift, are citizens of a heavenly country, look forward to a heavenly Jerusalem, and have their very names written in heaven.
One of the key theological themes in Hebrews is that all believers now have direct access to God under the New Covenant and, therefore, may approach the throne of God boldly (4:16; 10:22). One’s hope is in the very presence of God, into which he follows the Savior (6:19, 20; 10:19, 20). The primary teaching symbolized by the tabernacle service was that believers under the covenant of law did not have direct access to the presence of God (9:8), but were shut out of the Holy of Holies. The book of Hebrews may briefly be summarized in this way: Believers in Jesus Christ, as God’s perfect sacrifice for sin, have the perfect High-Priest through whose ministry everything is new and better than under the covenant of law.
This epistle is more than a doctrinal treatise, however. It is intensely practical in its application to everyday living (see chap. 13). The writer himself even refers to his letter as a “word of exhortation” (13:22; cf. Acts 13:15). Exhortations designed to stir the readers into action are found throughout the text. Those exhortations are given in the form of 6 warnings:
Another significant aspect of this epistle is its clear exposition of selected OT passages. The writer was clearly a skilled expositor of the Word of God. His example is instructive for preachers and teachers:
A proper interpretation of this epistle requires the recognition that it addresses 3 distinct groups of Jews: 1) believers; 2) unbelievers who were intellectually convinced of the gospel; and 3) unbelievers who were attracted by the gospel and the person of Christ but who had reached no final conviction about Him. Failure to acknowledge these groups leads to interpretations inconsistent with the rest of Scripture.
The primary group addressed were Hebrew Christians who suffered rejection and persecution by fellow Jews (10:32–34), although none as yet had been martyred (12:4). The letter was written to give them encouragement and confidence in Christ, their Messiah and High-Priest. They were an immature group of believers who were tempted to hold on to the symbolic and spiritually powerless rituals and traditions of Judaism.
The second group addressed were Jewish unbelievers who were convinced of the basic truths of the gospel but who had not placed their faith in Jesus Christ as their own Savior and Lord. They were intellectually persuaded but spiritually uncommitted. These unbelievers are addressed in such passages as 2:1–3; 6:4–6; 10:26–29; and 12:15–17.
The third group addressed were Jewish unbelievers who were not convinced of the gospel’s truth but had had some exposure to it. Chapter 9 is largely devoted to them (see especially vv. 11, 14, 15, 27, 28).
By far, the most serious interpretive challenge is found in 6:4–6. The phrase “once enlightened” is often taken to refer to Christians, and the accompanying warning taken to indicate the danger of losing their salvation if “they fall away” and “crucify again for themselves the Son of God.” But there is no mention of their being saved and they are not described with any terms that apply only to believers (such as holy, born again, righteous, or saints). This problem arises from inaccurately identifying the spiritual condition of the ones being addressed. In this case, they were unbelievers who had been exposed to God’s redemptive truth, and perhaps made a profession of faith, but had not exercised genuine saving faith. In 10:26, the reference once again is to apostate Christians, not to genuine believers who are often incorrectly thought to lose their salvation because of their sins.
This Grace to You article originally appeared here.
Copyright 2007, Grace to You. All rights reserved. Used by permission.
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
