
















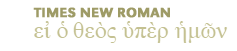
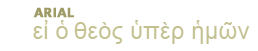

(See "Introduction to the Prophetical Books")
JONAH was the son of Amittai, of Gath-hepher in Zebulun (called Gittah-hepher in Jos 19:10-13 ), so that he belonged to the kingdom of the ten tribes, not to Judah. His date is to be gathered from 2Ki 14:25-27, "He (Jeroboam II) restored the coast of Israel from the entering of Hamath unto the sea of the plain, according to the word of the Lord God of Israel, which He spake by the hand of His servant Jonah, the son of Amittai, the prophet, which was of Gath-hepher. For the Lord saw the affliction of Israel, that it was very bitter: for there was not any shut up, nor any left, nor any helper for Israel. And the Lord said not that He would blot out the name of Israel from under heaven: but He saved them by the hand of Jeroboam the son of Joash." Now as this prophecy of Jonah was given at a time when Israel was at the lowest point of depression, when "there was not any shut up or left," that is, confined or left at large, none to act as a helper for Israel, it cannot have been given in Jeroboam's reign, which was marked by prosperity, for in it Syria was worsted in fulfilment of the prophecy, and Israel raised to its former "greatness." It must have been, therefore, in the early part of the reign of Joash, Jeroboam's father, who had found Israel in subjection to Syria, but had raised it by victories which were followed up so successfully by Jeroboam. Thus Jonah was the earliest of the prophets, and close upon Elisha, who died in Joash's reign, having just before his death given a token prophetical of the thrice defeat of Syria ( 2Ki 13:14-21 ). Hosea and Amos prophesied also in the reign of Jeroboam II, but towards the closing part of his forty-one years' reign. The transactions in the Book of Jonah probably occurred in the latter part of his life; if so, the book is not much older than part of the writings of Hosea and Amos. The use of the third person is no argument against Jonah himself being the writer: for the sacred writers in mentioning themselves do so in the third person (compare Jhn 19:26 ). Nor is the use of the past tense ( Jon 3:3, "Now Nineveh was an exceeding great city") a proof that Nineveh's greatness was past when the Book of Jonah was being written; it is simply used to carry on the negative uniformly,--"the word of the Lord came to Jonah. . . so Jonah arose. . . now Nineveh was," &c. ( Jon 1:1 3:3 ). The mention of its greatness proves rather that the book was written at an early date, before the Israelites had that intimate knowledge of it which they must have had soon afterwards through frequent Assyrian inroads.It seemed strange to KIMCHI, a Jew himself, that the Book of Jonah is among the Scriptures, as the only prophecy in it concerns Nineveh, a heathen city, and makes no mention of Israel, which is referred to by every other prophet. The reason seems to be: a tacit reproof of Israel is intended; a heathen people were ready to repent at the first preaching of the prophet, a stranger to them; but Israel, who boasted of being God's elect, repented not, though warned by their own prophets at all seasons. This was an anticipatory streak of light before the dawn of the full "light to lighten the Gentiles" ( Luk 2:32 ). Jonah is himself a strange paradox: a prophet of God, and yet a runaway from God: a man drowned, and yet alive: a preacher of repentance, yet one that repines at repentance. Yet Jonah, saved from the jaws of death himself on repentance, was the fittest to give a hope to Nineveh, doomed though it was, of a merciful respite on its repentance. The patience and pity of God stand in striking contrast with the selfishness and hard-heartedness of man.
Nineveh in particular was chosen to teach Israel these lessons, on account of its being capital of the then world kingdom, and because it was now beginning to make its power felt by Israel. Our Lord ( Mat 12:41 ) makes Nineveh's repentance a reproof of the Jews' impenitence in His day, just as Jonah provoked Israel to jealousy ( Deu 32:21 ) by the same example. Jonah's mission to Nineveh implied that a heathen city afforded as legitimate a field for the prophet's labors as Israel, and with a more successful result (compare Amo 9:7 ).
The book is prose narrative throughout, except the prayer of thanksgiving in the second chapter ( Jon 2:1-9). The Chaldaeisms in the original do not prove spuriousness, or a later age, but were natural in the language of one living in Zebulun on the borders of the north, whence Aramaicpeculiarities would readily arise; moreover, his message to Nineveh implies acquaintance with Assyrian. Living as Jonah did in a part of Israel exposed to Assyrian invasions, he probably stood in the same relation to Assyria as Elijah and Elisha had stood to Syria. The purity of the language implies the antiquity of the book, and the likelihood of its being Jonah's own writing. Indeed, none but Jonah could have written or dictated such peculiar details, known only to himself.
The tradition that places the tomb of Jonah opposite to Mosul, and names it "Nebbi Junus" (that is, "prophet Jonah"), originated probably in the spot having been occupied by a Christian church or convent dedicated to him [LAYARD]. A more ancient tradition of JEROME'S time placed the tomb in Jonah's native village of Gath-hepher.
The Blue Letter Bible ministry and the BLB Institute hold to the historical, conservative Christian faith, which includes a firm belief in the inerrancy of Scripture. Since the text and audio content provided by BLB represent a range of evangelical traditions, all of the ideas and principles conveyed in the resource materials are not necessarily affirmed, in total, by this ministry.
Loading
Loading
| Interlinear |
| Bibles |
| Cross-Refs |
| Commentaries |
| Dictionaries |
| Miscellaneous |
